Ransomware Attacks & Cryptocurrencies a Match Made in Heaven

The Rise in Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system until a sum of money is paid.
Ransomware attacks have been on the rise and all signs point to it not slowing down anytime soon. According to Radware’s Global Application and Network Security Report, the number of companies that fell victim of ransomware and paid the ransom, increased by 40% from 2016. In 2018, executives don’t expect this to go away with 26% believing it will be the biggest threat to their business. And with the costs expected to exceed $5 billion in 2017, up from $325 million on 2015, the financial motivation is certainly attractive for these hackers.
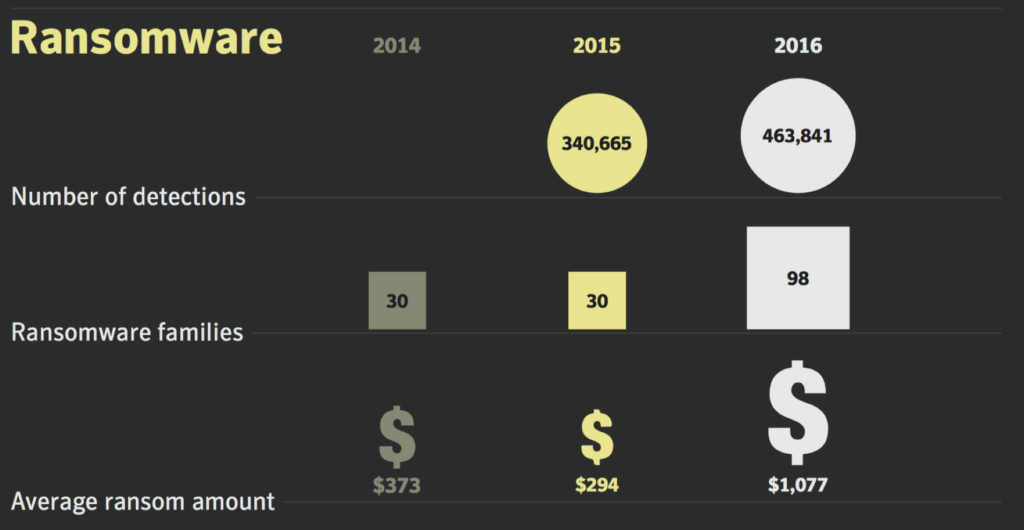
Symantec’s 2017 Internet Security Threat Report highlights an increase in ransomware detections, families, and the average ransom amount per attack which is now has an average above $1,000.
Some of the more popular ransomware attacks are WannaCry and Petya and NotPetya. Jonathan Penn, Director of Strategy at Avast states that WannaCry was “easily the worst ransomware attack of all time”. Petya is ransomware that once it infects a computer displays a message explaining how the victim can pay in Bitcoin to get their data back. WannaCry demanded between $300 – $600 per computer and Petya demanded $300 in bitcoins, however the success rate for these hackers was low. Only about 0.4% paid the Petya ransom. This is mainly because the victims don’t trust that the hackers will actually unlock their data.
Cryptocurrencies & Ransomware
Cryptocurrencies are a form of digital money that is designed to provide secure financial transactions and in most cases do this anonymously. This makes it the “go-to” currency for hackers. Being paid in crypto currency, like Bitcoin, means the money can’t be traced back to the hacker, drastically reducing their risk.
Some organizations are even stockpiling Bitcoin’s to prepare for future attacks so they can pay off the attackers. The problem for these organization’s is hackers are moving away from Bitcoin to more anonymous cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum, Monero, and Zcash.
According to some reports, 93% of phishing emails contain ransomware. The best defense against these phishing attacks is to protect your email system and your employees. We previously wrote about email security best practices. This would be a good place to start when it comes to securing your email system. By adding an additional layer of protection, like Graphus, you can drastically reduce the number of successful threats against your organization by detecting and mitigating spoofing, phishing attacks, emails scams and emails with malicious attachments or links.
Want to protect your organization from cyber attacks? Click the button below.










